What is the Chemical Makeup of Marijuana?
People often think of marijuana only in terms of how it makes them feel but have you ever wondered about the biological and chemical makeup of marijuana? While cannabis has been used and cultivated for at least 6000 years, it’s just in these modern times that we’re finding out about its chemical properties.
Jump to our visual story on “What is the Chemical Makeup of Marijuana?” for a snapshot in under a minute.
Marijuana Chemistry 101
According to National Institute on Drug Abuse, marijuana is the name given to the dried leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds from the Cannabis sativa or Cannabis indica plant. A study mentioned that marijuana has over 400 chemical entities and more than 60 of them are cannabinoid compounds. Two main cannabinoids widely studied are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Before we get into the chemical makeup of marijuana, let’s examine the different types of cannabis plants and our endocannabinoid system.
Types of Cannabis Plants
According to Zerrin Atakan, author of the study, Cannabis, a complex plant: different compounds and different effects on individuals, there are two types of marijuana plants; Cannabis indica and Cannabis sativa. The study outlined several differences between them namely physical and chemical.
Physical Differences
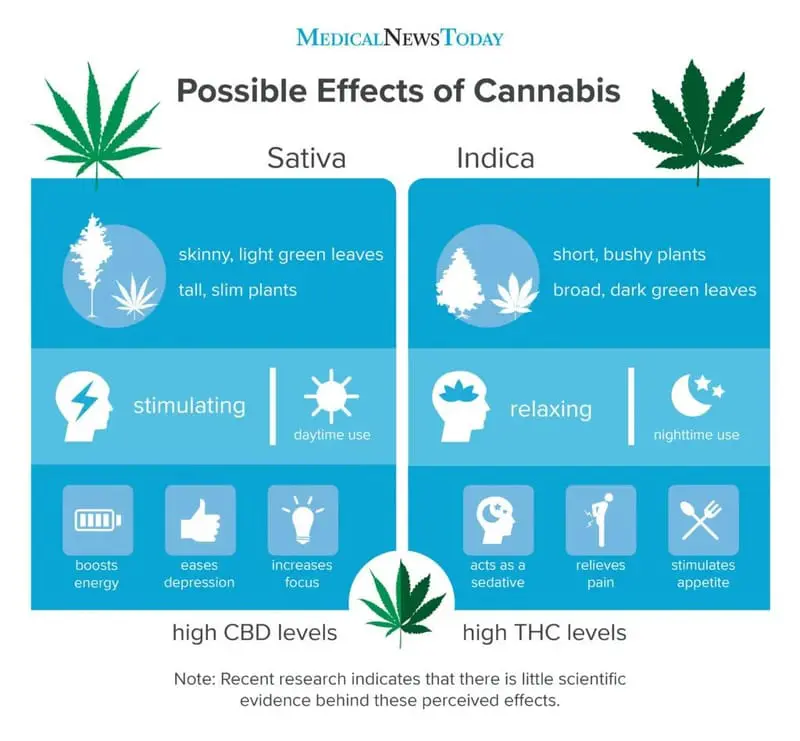
Indica-dominant strains are short plants with broad, dark green leaves. On the other hand Sativa-dominant strains are typically taller and have thin leaves with a pale green colour. If you’d like a visual representation, you can check out the diagram below.
Chemical Differences
The physical difference isn’t the only thing that separates the two subspecies. They are also chemically different. The study mentioned that Indica-dominant strains have a higher concentration of cannabidiol (CBD) while Sativa-dominant strains tend to have more THC. Needless to say but the Sativa strains are the preferred strain for getting high. Due to these chemical differences, Sativa and Indica give users a different feeling as you can observe from the diagram above.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The human body has its very own endocannabinoid system. According to Healthline, the endocannabinoid system is a complex cell signalling system that has three main components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. You can examine the receptors and where they are located in the body in the diagram below.
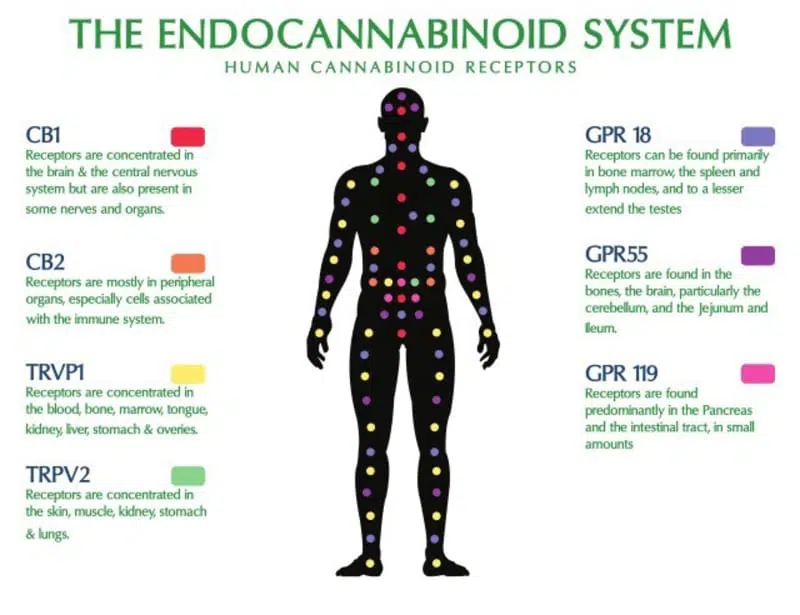
What is interesting about this system is that it was actually discovered in the 1990s while scientists were studying THC. Since it’s recently discovered, it’s not certain how it all works. The endocannabinoid system is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis (maintaining the stability of the body’s internal environment).
What does the Endocannabinoid System Do?
According to Healthline, researchers have linked the endocannabinoid system to the following:
- appetite and digestion
- metabolism
- chronic pain
- inflammation and other immune system responses
- mood
- learning and memory
- motor control
- sleep
- cardiovascular system function
- muscle formation
- bone remodeling and growth
- liver function
- reproductive system function
- stress
- skin and nerve function
The Endocannabinoid System Basics
Healthline says your body makes its own endocannabinoids, namely anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG) which binds to your receptors and do their jobs. They can either bind to CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in your central nervous system or CB2 receptors, which are primarily found in your peripheral nervous system. When it’s time for the endocannabinoids to be broken down by enzymes, fatty acid amide hydrolase breaks down AEA and 2-AG is broken down by monoacylglycerol acid lipase.
So you may be wondering what does this have to do with cannabis? Cannabinoids from marijuana also bind to your receptors when consumed.
Chemical Makeup of THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
THC, an aromatic terpenoid is one of the main components of marijuana and it’s most popularly known for making you feel high. It’s a lipid compound that may be used by the marijuana plant for defense against things like insects and UV light. THC occurs mainly as tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA, 2-COOH-THC, THC-COOH). THCA, when heated, such as when smoking, becomes THC due to decarboxylation.
According to Healthline, THC has 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms (just like CBD). THC binds to both the CB1 and CB2 receptors in your body. You may feel euphoric or high because of THC binding to CB1. You may feel hungry, paranoid, anxious or reduction in pain when using marijuana, it’s all due to the THC binding to your cannabinoid receptors.
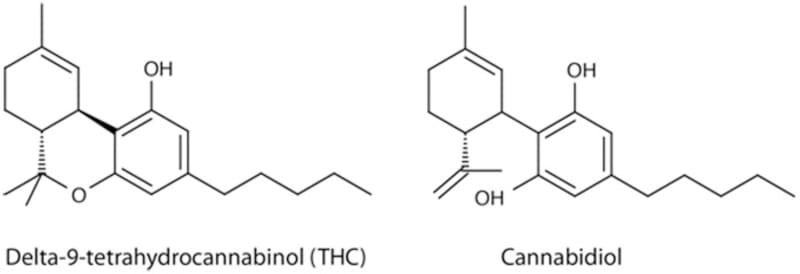
THC also occurs in two forms, Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. According to Cancer.gov, even though delta-8-THC binds to receptor CB1, “lower psychotropic potency” than delta-9-THC.
Chemical Makeup of CBD (Cannabidiol)
A study stated that CBD is the main non-psychotropic compound in the Cannabis sativa plant and it accounts for 40% of the extract. According to Healthline, CBD also has 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms.
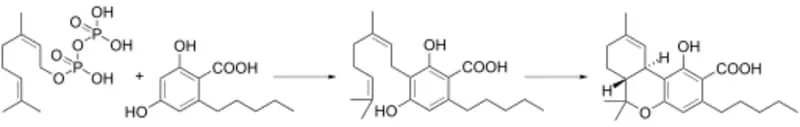
CBD is present due to non‐enzymatic decarboxylation of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). You can take a look at the process in the diagram below:
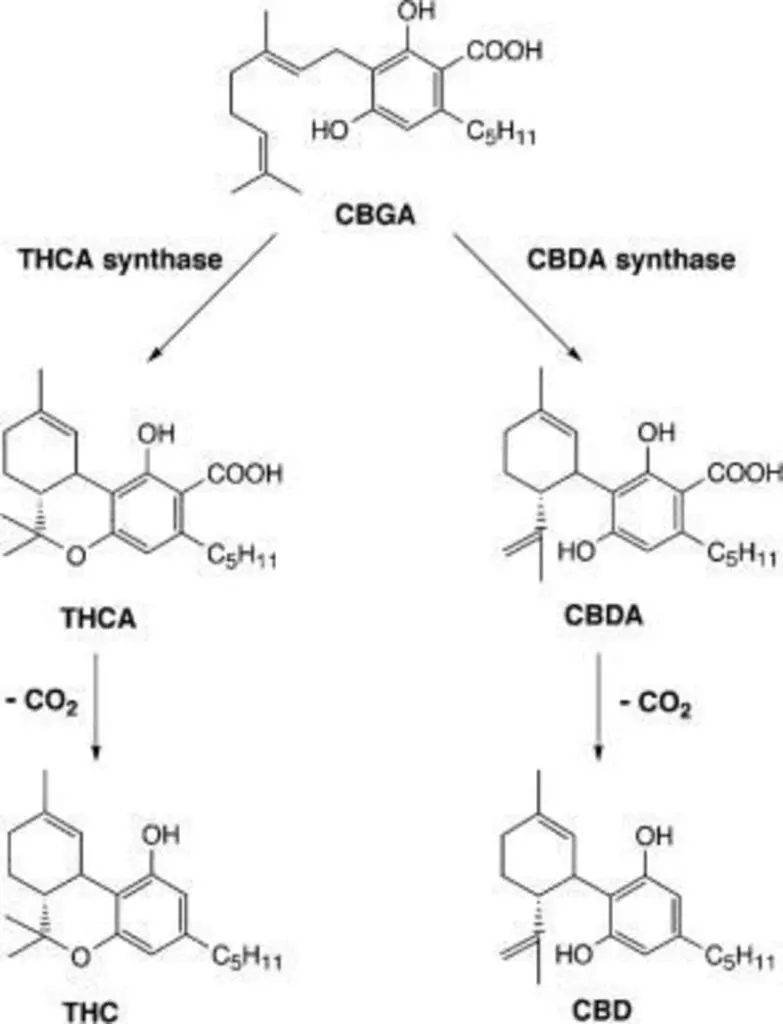
CBD is not responsible for the high feeling, it can be sort of an antagonist to THC. According to Healthline, “CBD binds very weakly, if at all, to CB1 receptors”, the article went on to say that CBD needs THC to bind to the CB1 receptor and then it can counteract some of the psychoactive effects of THC.
There is still some mystery surrounding just how CBD binds, Healthline reports, “Experts aren’t completely sure how CBD interacts with the ECS. But they do know that it doesn’t bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors the way THC does.”. They believe that CBD may prevent the disintegration of endocannabinoids or it may just bind to a receptor that hasn’t been discovered yet.
Conclusion
While there is still a lot of marijuana research needed, scientists are well on their way to figuring out the chemical makeup of marijuana. The use of cannabis is definitely not new but understanding it from a chemical and molecular level is much newer. You probably won’t remember all the scientific details when consuming weed. However, whenever you’re curious as to what is going on where chemistry is concerned, feel free to come back and read this article.